Contents
Overview of Japanese Consumption Tax
Like many consumption tax (value-added tax or VAT) systems around the world, Japanese Consumption Tax (JCT) is levied on products and services consumed in Japan. As an indirect tax, JCT is not paid directly to the tax authorities by the taxpayer (the consumer), but collected and remitted by producers, wholesalers, and retailers.
As of 2022, the applicable JCT rate is 10%, but a lower tax rate of 8% applies for selected products such as food, beverages, and newspaper subscriptions. In addition, certain transactions are non-taxable, such as the sale and lease of land, securities, insurance, etc.
Businesses that are “JCT enterprises” (see next section) are obligated to pay tax on their taxable sales. On the other hand, JCT enterprises can also claim tax credits on their taxable purchases. As such, businesses may elect to become a JCT enterprise if their purchases exceed their sales or if they plan to export products overseas.
JCT Enterprise
Generally, a business becomes a JCT enterprise if any of the following applies:
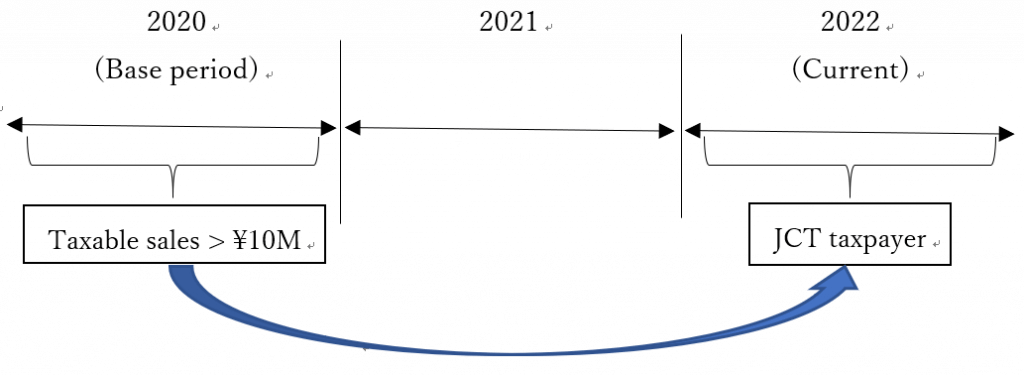
a) Their taxable sales within the base period is greater than 10 million yen. (The base year is generally defined as the period two years prior to the current period.)
b) Their taxable sales* within the specified period is greater than 10 million yen. (The specified period is generally defined as the first six months of the period prior to the current period.)
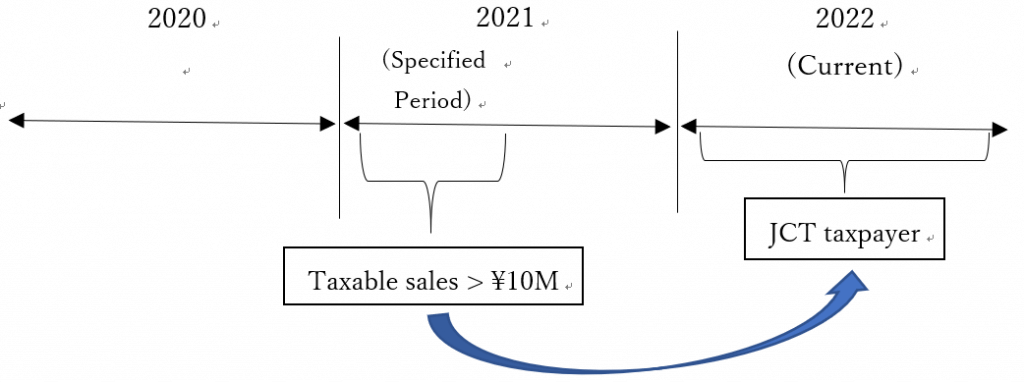
* Total salary payment can be used instead of taxable sales as the judgement criteria, whichever yields the more advantageous result for the business.
c) They have filed a “Report on the Selection of Taxable Proprietor Status for Consumption Tax” voluntarily. A business may choose to file this form if their input tax exceeds their output tax (e.g. if exports comprise a large part of their sales while purchases are made in Japan).
Qualified Invoice System
In order to claim tax credit on their purchases, businesses are required to store invoices from their suppliers that meet certain requirements. Starting October 1, 2023, these requirements will be reinforced under the Qualified Invoice System.
Only invoices that satisfy the conditions below will be deemed as “qualified invoices”:
1) Contain the required information
2) Be issued by a registered invoice issuer
Required information (new requirements in bold):
– Invoice issuer name and registration number
– Transaction date
– Transaction details
– Applicable tax rate
– Consumption tax amounts broken down into respective tax rates
– Recipient of invoice
Registered invoice issuer
Enterprises must register with the tax authority in order to become a registered invoice issuer. Once approved, the enterprise will be given a registration number, which shall be included in invoices issued. Please note that as a registered invoice issuer, you will be deemed a JCT enterprise and be required to file consumption tax returns.
On-demand Seminar Information

A Guide to the Qualified Invoice System (On-demand Seminar)
The Qualified Invoice System, starting October 2023, introduces new changes to the Japanese consumption tax rules and will affect many businesses across Japan.
The system requires a redesign of existing invoices, as well as a review of the business’ consumption tax status and suppliers.
This online seminar aims to give you an overall understanding of the Qualified Invoice System and provide measures to help you navigate the new requirements.
>>Click here for seminar details and registration
TOMA’s services
TOMA Consultant Group can assist you with the following:
– Application to become a JCT enterprise or a registered invoice issuer
– Filing of consumption tax returns
– Assessment of whether becoming a JCT enterprise would be right for you
– Assessment of the best taxation method to use
– Other related consultation
Please contact us for a free consultation on how we can best support your business in Japan.